Conditions We Treat Parathyroid Disease
Overview
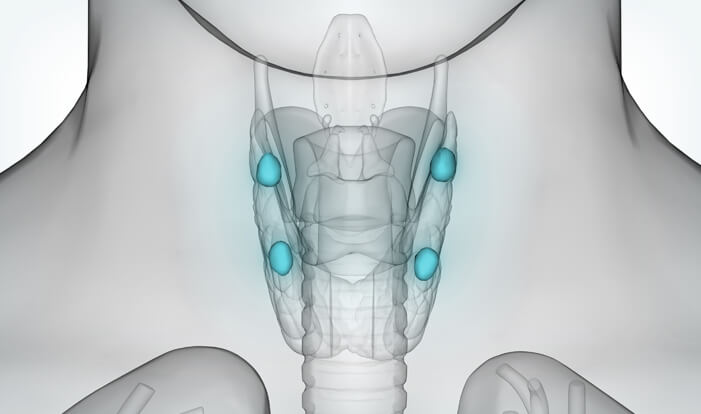
The thyroid and parathyroid glands serve entirely different purposes within the body. The four pea-shaped parathyroid glands (set behind the thyroid) regulate calcium levels in our blood and bones. When the parathyroid does not function properly and results in a hormone imbalance, the body’s calcium levels get thrown off. The ideal calcium balance helps the heart, nervous system, bones, and kidneys function properly. Parathyroid diseases that require surgical consultation include: Hyperparathyroidism – Too much parathyroid hormone (PTH) produced.
Symptoms
Hyperparathyroidism
Symptoms of the most common parathyroid disease range from nonexistent to mild to severe. It’s important to note that the actual levels of calcium and PTH do not correlate with severity of symptoms. Someone can have only mildly elevated levels yet experience debilitating symptoms. They can include fatigue, depression, bone and joint pain, constipation, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, confusion, increased thirst and urination, kidney stones, osteoporosis.
Hypoparathyroidism
Tingling in fingertips, toes, and lips; muscle cramps and spasms around the mouth but also in the hands, legs, and feet; depression; anxiety; brittle nails; dry hair and skin; fatigue; patchy hair loss; memory loss; painful menstruation; headaches; cataracts; weakened tooth enamel.

Causes
Primary hyperparathyroidism results from the parathyroid glands making too much parathyroid hormone (PTH), which leads to excess calcium in the body. This can happen due to a benign tumor, overactive parathyroid glands, or parathyroid cancer (very rare). Secondary parathyroidism can be caused by outside factors such as kidney disease, calcium deficiency, or vitamin D deficiency. Any of these will result in the parathyroid making too much PTH.

Diagnosis
Following a physical examination and discussion of symptoms, blood work is typically the next step toward a parathyroid disease diagnosis. Elevated calcium levels on their own do not necessarily indicate hyperparathyroidism, but high calcium levels combined with high parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels point to that disorder. These tests are followed by imaging studies including a sestamibi scan and neck ultrasound.

Treatment Options
The vast majority of hyperparathyroidism cases can be cured through surgery (parathyroidectomy). Only the enlarged glands or those with a tumor on them will be removed.
Dr. Uecker has many years of experience of surgical treatment of parathyroid disease. For most patients, he offers a minimally invasive surgical approach. He regularly works with a multi-disciplinary team to provide comprehensive care to patients suffering from parathyroid problems.
